Bladder problems are common in people with MS. They usually consist of urgency, frequency, incomplete emptying, and sometimes incontinence. Oxytrol (oxybutynin) is often prescribed for bladder dysfunction when urinary tract infection has been ruled out by a physician.
 Oxybutynin is an antimuscarinic medicine that reduces involuntary contractions of the bladder muscles and increase bladder capacity. It is used in to treat overactive bladder that leads to urinary urgency, frequency, and incontinence. Oxybutynin works by relaxing the bladder muscles to slow desire, frequency, and urgency to urinate.
Oxybutynin is an antimuscarinic medicine that reduces involuntary contractions of the bladder muscles and increase bladder capacity. It is used in to treat overactive bladder that leads to urinary urgency, frequency, and incontinence. Oxybutynin works by relaxing the bladder muscles to slow desire, frequency, and urgency to urinate.
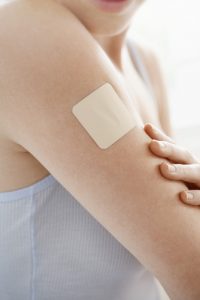
Oxytrol (oxybutynin) is delivered by a medicated patch that adheres to the skin. The active ingredient enters through the skin and goes into the bloodstream bypassing the liver and digestive tract. Each oxytrol skin patch lasts for 4 days.
Side effects can include itching, rash, or redness where the patch is placed. Uncommon effects include dry mouth and constipation.
Other less common side effects are sleepiness, dizziness, and blurry vision that may be increased with alcohol drinking.
Only one Oxytrol generic is FDA approved but it is not yet available due to patent protection.
Read the latest news on oxybutynin and bladder dysfunction.
Note: Multiple Sclerosis News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.