Multiple sclerosis symptoms
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys myelin, a fatty substance that covers and protects nerve fibers and is critical for the promotion of a quick and efficient transmission of nerve impulses. Without myelin, nerve communication is affected, resulting in a wide range of symptoms.
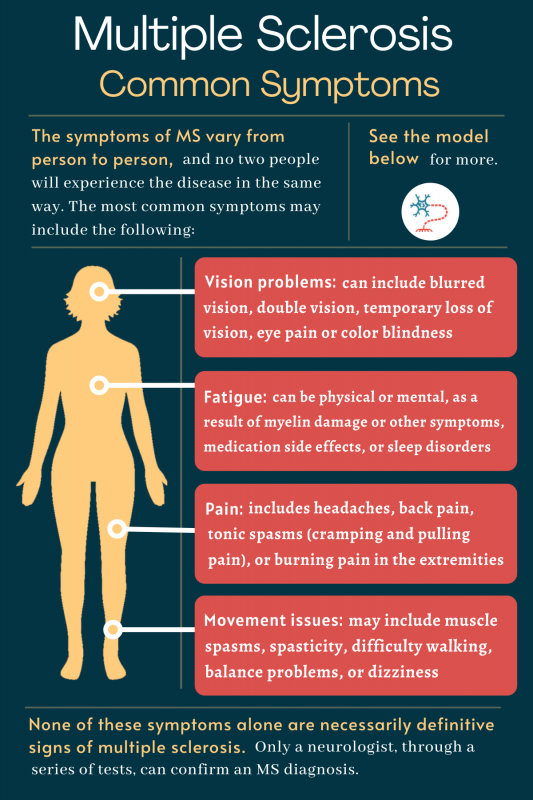
MS symptoms vary from person to person, depending on which specific parts of the nervous system are most affected. Severity also varies widely, meaning that everyone with MS will have a different experience. Disease symptoms include numbness and tingling, fatigue, walking difficulties, pain, vision problems, among others.
How does MS type affect symptoms?
MS is broadly classified into four main types based on the phase and severity of disease progression. They are:
Clinically isolated syndrome
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) is considered the first clinical presentation of disease characterized by inflammatory demyelination (myelin loss). CIS can be thought of as a first episode of neurological symptoms that are suggestive of MS. People with CIS may never have another episode of symptoms, or they could progress to full MS.
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) is the most common type of MS and is characterized by relapses (also called exacerbations), which are defined by the appearance of new symptoms, or the return of old symptoms, for at least 24 hours and without a change in body temperature or infection. Relapses are followed by remissions, which are periods of partial or complete recovery from symptoms.
Secondary progressive multiple sclerosis
Secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS) is a stage of the disease that follows RRMS. With this type of MS, a person’s symptoms steadily worsen. Relapses may still occur in SPMS, but changes in symptoms are usually much less drastic than in RRMS and symptoms do not disappear even in the remission periods.
Primary progressive multiple sclerosis
Like SPMS, primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS) is characterized by symptoms that become worse over time, without the periods of relapse and remission that characterize RRMS. In PPMS, disease progression starts right from disease onset — hence the term “primary” progressive.
What are the early signs of MS?
A concrete list of early signs of MS does not exist, given that disease manifestations can be variable and quite different between affected individuals. A number of symptoms, however, are common to the disease and may be considered early signs of MS. These are:
- excessive fatigue
- difficulty walking or frequent stumbling (loss of balance)
- numbness and tingling (a feeling of pins and needles)
- pain
- stiffness or spasms
- vision problems
- slowed thinking
People concerned they may be experiencing symptoms of the disease are advised to talk with their healthcare provider and keep a record of the occurrence, severity, and duration of their symptoms.
Only a medical professional with specialized training in neurology or nervous system disorders can confirm an MS diagnosis.
What are the common symptoms of MS?
Specific symptoms will vary from person to person, depending on factors like where in the body the nervous system is being damaged. The severity of symptoms also varies widely, meaning that everyone with MS will have a different experience.
The inflammatory attack on the nervous system can cause disease relapses, also called exacerbations or flare-ups, which are periods of time when one or more symptoms appear or get substantially worse. To constitute a relapse, these symptoms must last for at least a day, and may continue for weeks or months.
The most common symptoms of multiple sclerosis include the following:
| MS symptoms | Percentage of patients who experience the symptom |
|---|---|
| Movement problems | ~87% |
| Fatigue | 80% |
| Chronic pain | 63% |
| Vision problems | 58% |


Living with MS
Symptoms of MS vision problems

Living with MS
High-dose vitamin D delays MS progression
Movement problems
Muscle spasms and spasticity, an abnormal increase in muscle tone or stiffness that affects muscle movements, are among the most common MS symptoms. It is estimated that 60%–90% of MS patients will experience spasticity at some point.
Damage to parts of the brain that help to regulate balance can cause dizziness, a range of sensations that include feeling light-headed, faint, off-balance, and disoriented. Some people with MS experience vertigo, a more severe form of dizziness that is characterized by an intense sensation of spinning, which can lead to:
- balance and vision problems
- motion sickness
- nausea
- vomiting
As a result of spasticity and balance problems, as well as fatigue, muscle weakness, and other symptoms, many people with MS experience difficulty walking, especially in latter stages of the disease.
Tremors (uncontrolled shaking) can occur in some people with MS. Additionally, muscle weakness and neurological problems in the face and jaw can lead to abnormal speech or dysphagia (swallowing problems).
Fatigue
Fatigue is defined as mental or physical exhaustion that prevents a person from performing everyday activities. It is one of the most common symptoms in MS, affecting about 80% of patients. Among MS patients, fatigue is linked to under-employment, early retirement, and reduced quality of life.
MS-related fatigue could be “primary,” also called lassitude, which is a direct result of myelin damage. This fatigue is unique to MS and different from that experienced by people without MS: it is sudden, more severe, aggravated by heat or humidity, and unaffected by restful sleep. By contrast, “secondary” MS-related fatigue is an indirect result of other MS symptoms, such as depression, stress, recent relapses, side effects of medication, and sleep disorders.
MS fatigue can be managed through medication and/or lifestyle changes (such as exercise, diet, naps, and cold showers). Experts also recommend evaluating and treating any secondary causes (such as drug side effects, depression, and sleep disorders) to help manage fatigue in MS.
Pain
Up to two-thirds of people with MS experience a wide range of pain-related symptoms, from headache and back pain to painful tonic spasms (cramping and pulling pain), and continual burning pain in the extremities. MS patients may develop:
- Neuropathic pain, where the sensation of pain is caused by damage to the parts of the nervous system normally responsible for detecting pain. This is the most common type of pain experienced by people with MS. It typically occurs in the legs and is felt as a persistent and burning pain.
- Musculoskeletal pain, where pain occurs as a result of abnormal muscle activity like spasticity.
- Paroxysmal (sudden) pain, which is less common, but is most frequently experienced by MS patients as facial pain caused by trigeminal neuralgia (a condition characterized by damage in the nerve that carries information from the eyes, cheek, and jaw to the brain).
Good mental health practices with exercise, staying active socially, body massages, chiropractic treatments, hydrotherapy, acupuncture, and/or medications can help to manage MS pain and improve quality of life.
Most common analgesics (painkillers) are usually not enough to ease pain caused by nerve damage in the central nervous system, so drugs that treat seizures, antidepressants, and some benzodiazepines are among the common first choices for pain management in MS.
Other abnormal sensations
Beyond pain, people with MS may experience other abnormal sensations, like numbness, tingling, or uncontrolled itching. They also may experience dysesthesia, which is an unpleasant and possibly painful sensation often described as a burning and aching feeling or, if affecting the trunk, a “girdling” sensation across the body (popularly known as the “MS hug”).
Another abnormal sensation that can occur in people with MS is Lhermitte’s sign: a sudden sensation that feels like an electric shock passing down the back of a person’s neck and into the spine, which may then radiate out into the limbs. Lhermitte’s sign is usually triggered by bending the head forward towards the chest.
Heat intolerance in MS is common. Heat, in whatever form, can cause MS symptoms to worsen. This can be triggered by anything that raises the body’s temperature, including exercise, sunbathing, hot baths, and fevers. Common effects of heat sensitivity include:
- increased fatigue
- blurred vision
- loss of balance
- memory and concentration difficulties
Bladder, bowel, and sexual complaints
People with MS often experience bladder problems, frequent urination or difficulty urinating, and bowel problems, like constipation.
Sexual health problems are also common in MS. Damage to nerve impulses can directly affect arousal and orgasm, and other symptoms — from emotional problems to fatigue to movement difficulties — can cause challenges in sexual relationships.
People with MS may experience:
- decreased or painful genital sensation
- difficulty achieving orgasm
- erectile dysfunction
- vaginal dryness
MS does not directly affect fertility, though symptoms like erectile dysfunction may still pose obstacles for people trying to have children.
Emotional and cognitive problems
Mental health problems, such as anxiety and mood swings, are common in people with MS.
Depression — characterized by long periods of sadness, apathy, and other negative thoughts — is especially common. Depression occurs more frequently in MS than in the general population or in other diseases. It can be directly caused by the underlying damage to the nervous system, but some medications can also contribute to depression in certain individuals.
Some people with MS may experience pseudobulbar affect, a sudden burst of uncontrollable laughter or crying, often for no apparent reason.
Damage to the nervous system can cause difficulty with thinking or reasoning, learning, problem-solving, and planning. More than half of MS patients will experience problems with cognition. These changes are usually mild, but more severe cognitive impairment can occur.
Vision and hearing problems
MS can cause damage to the optic nerves, which connect the eyes to the brain. Consequently, the following vision problems may develop in MS:
- blurred vision
- double vision
- temporary loss of vision
- eye pain (especially when moving the eye)
- eye twitching
- color blindness
Hearing loss can occur in MS, though less frequently than vision problems.
How are MS symptoms different between men and women?
MS is up to three times more common in females than it is in males. In general, women seem to be more likely to develop autoimmune diseases. The reason for this difference likely has to do with hormonal and chromosomal differences between the sexes. Although most of the symptoms of MS in women are similar to those in men, special concern is given to issues particular to women, including the following:
- Menstrual and menopausal issues
- Sexual problems
- Pregnancy-related symptoms
| MS symptoms in men | MS symptoms in women |
|---|---|
| More likely to have PPMS | More likely to have RRMS |
| May experience greater brain atrophy | May develop more lesions or scar tissue |
| Higher incidence of T1 lesions | Higher incidence of T2 lesions |
| May experience more cognitive issues | May develop more eye symptoms |
Symptoms of MS in women
Menstrual and menopausal issues
Research is still insufficient regarding the impact of MS on the endocrine system.
Some women with MS report that their disease symptoms are worse at certain points in their menstrual cycle, particularly in the week leading up to and the first few days into the cycle. Reasons for this worsening of symptoms are not yet completely understood, but fluctuations in the immune system and core body temperature across the menstrual cycle have been suggested as possible causes.
Some women with MS also report that menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes, exacerbate their MS symptoms. During menopause, the body stops producing estrogen in significant quantities.
Additional research is necessary to understand the specific ways in which MS might affect women’s bodies.
Sexual problems
Women with MS may experience reduced or painful sensation in the vaginal/clitoral area, as well as vaginal dryness. Although no specific medications are available for these symptoms, vaginal dryness can be relieved with liberal use of water-based lubricants.
Problems with orgasm may be overcome by stimulating sensitivity — spending more time on foreplay and using a vibrator to overcome slow arousal and impaired sensation.
Being able to discuss sex-related issues with healthcare providers and others is important.
Pregnancy-related symptoms
In general, MS does not affect a woman’s fertility. There seems to be no evidence to suggest that women with MS are at a higher risk of pregnancy complications, such as being diagnosed with gestational diabetes, requiring an emergency Cesarean section (C-section), or having a preterm or stillbirth delivery.
As MS is unique to each individual, women who plan to become pregnant should discuss with their healthcare team the potential risks and benefits of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) to decide on the best treatment plan. Some studies have shown that certain DMTs may be safer than others to take while pregnant, trying to conceive, or breastfeeding, but more research is needed.
Some women with MS report that some of their symptoms — including fatigue, balance, back pain, and bladder and bowel problems — feel worse during pregnancy. Women with MS tend to have fewer relapses, or disease flare-ups, during pregnancy, although the risk of relapse increases in the first three to six months after delivery of the baby.
Symptoms of MS in men
While women tend to be diagnosed with RRMS/SPMS in higher numbers than men, men are more likely to be diagnosed with PPMS, although the exact reasons remain unclear.
Men are also more likely to experience increased disease progression and seem to have greater cognitive issues.
Men with MS often face sexual difficulties, including erectile dysfunction, difficulty reaching orgasm, and decreased sexual desire. As is the case for women, lubricants and stimulating sensitivity, specific medication for erectile dysfunction, and being able to discuss sex-related issues with healthcare providers and others are important factors to try to achieve a better sexual life.
Of note, patients diagnosed with late-onset MS (after age 50) have a similar disease course regardless of sex, with disability accumulating at a similar rate in men and women. It is thought that this might be due to hormone changes during menopause, which make hormonal differences between sexes less striking.
Multiple Sclerosis News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
FAQs about MS symptoms
MS signs and symptoms vary greatly and can range from mild to severe. They can appear quickly and may disappear after a few days or weeks. In some cases they may only reappear years later. MS symptoms are triggered by the loss of myelin (a protective coating) on nerve fibers in the central nervous system — which encompasses the optic nerves, brain, and spinal cord — resulting in a lesion that may interfere with the transmission of nerve signals and therefore, depending on its location, cause the disease symptoms.
In patients with relapsing-remitting MS, disease symptoms usually improve after each relapse — a period referred to as remission in which partial or complete recovery from symptoms occurs. In patients with primary progressive MS, however, symptoms typically get worse over time without any obvious relapses or remissions periods. Effective treatments can help manage and to some extent prevent symptom progression.
Disease progression can vary significantly between people and according to the type of MS. People may experience periods where the disease symptoms are stable — these can last for years — but also periods of rapid symptom development (within hours or days). As a chronic, progressive disease, MS leads to increasing disability over time.
Related Articles
-
October 8, 2021 by Bionews Staff
Newly Diagnosed With Multiple Sclerosis
-
September 27, 2021 by Bionews Staff
Pain and Multiple Sclerosis
-
September 29, 2021 by Bionews Staff
Sex, Intimacy, and Multiple Sclerosis
-
September 22, 2021 by Bionews Staff
Living Well With Multiple Sclerosis

 Fact-checked by
Fact-checked by