FAQs about McDonald criteria
Yes. The McDonald criteria are a formal set of guidelines that have been regularly updated to help clinicians make an accurate MS diagnosis as early as possible. Depending on a person’s symptoms and test results, the help criteria outline which additional tests should be performed before confirming a diagnosis. Using these guidelines helps ensure MS is recognized quickly and accurately.
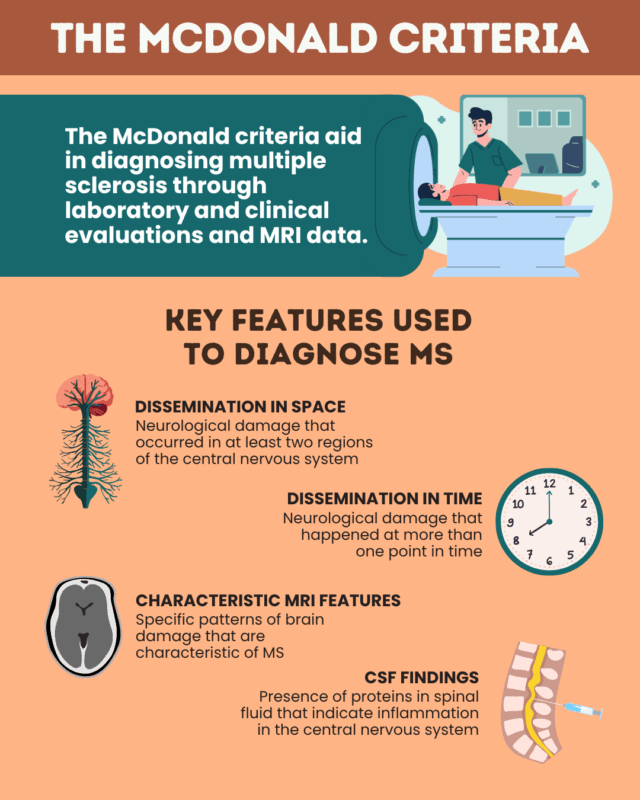
Dissemination in time means that nerve damage typical of MS has occurred at different points in time. Meanwhile, dissemination in space means that the damage has occurred in multiple parts of the central nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. These two findings can be used together or in combination with other MS-specific features to help doctors establish a diagnosis.
Yes, relapses are an important clinical feature that can help fulfill the McDonald criteria. For example, if a person has experienced two or more relapses, they have evidence of inflammatory activity occurring at multiple points in time, thereby meeting the criteria for dissemination in time.
Yes. Optic neuritis, which refers to inflammation in the nerves that carry information from the eyes to the brain, can be used to support an MS diagnosis under the 2024 McDonald criteria. The optic nerves are now one of the five regions considered when assessing dissemination in space, making optic nerve involvement an important clue that supports an MS diagnosis.
The 2024 update aims to help doctors confirm an MS diagnosis sooner while reducing the risk of misdiagnosis. Major changes include recognizing the optic nerve as an additional region for assessing dissemination in space, new guidance on specific MRI findings and test results, and introducing a single, unified framework to diagnose all types of MS and all age groups, replacing the separate criteria used previously. Importantly, these updates do not invalidate diagnoses made under earlier versions of the criteria.
 Fact-checked by
Fact-checked by