CBD and Multiple Sclerosis: What You Need to Know
Written by |

Topics related to the use and effectiveness of cannabidiol (CBD) and medical marijuana are of increasing interest to many people, including those with multiple sclerosis (MS).
A web-based survey hosted by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, with results published in 2017, indicated that as many as 66% of MS patients at that time were using cannabis for the treatment of their symptoms. A similar 2016 survey of Canadian patients with MS indicated that 50% would consider the use of cannabis if the legal status were clear and scientific evidence available.
Here are some frequently asked questions about cannabidiol and MS.
What is CBD?
CBD is a compound isolated from the Cannabis sativa plant that does not contain the psychoactive chemical tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), known to produce the “high” users feel. For this reason, it is regulated differently from THC-containing marijuana. CBD comes from hemp varieties of the cannabis plant, as opposed to the strains known as marijuana, which have higher amounts of THC.
How does CBD reportedly work?
The mechanisms by which CBD affects the body are still under investigation. The compound is thought to bind to and activate the endocannabinoid receptors. Two endocannabinoid receptors have been identified — CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are located in the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord), intestines, connective tissues, and gonads and several other glands. CB2 receptors are located in the spleen, tonsils, thymus, and immune cells; only a few are in the brain.
Data suggests that CBD does bind to the receptors but does not directly activate them. Instead, it appears to modulate or adjust how the receptors respond to stimulation from other compounds such as THC, for example.
Is it legal?
In the U.S., this depends on the individual state and the intended use of cannabis — whether it is medicinal or recreational. Federal legislation has legalized CBD products derived from hemp, but individual states have their own legislation.
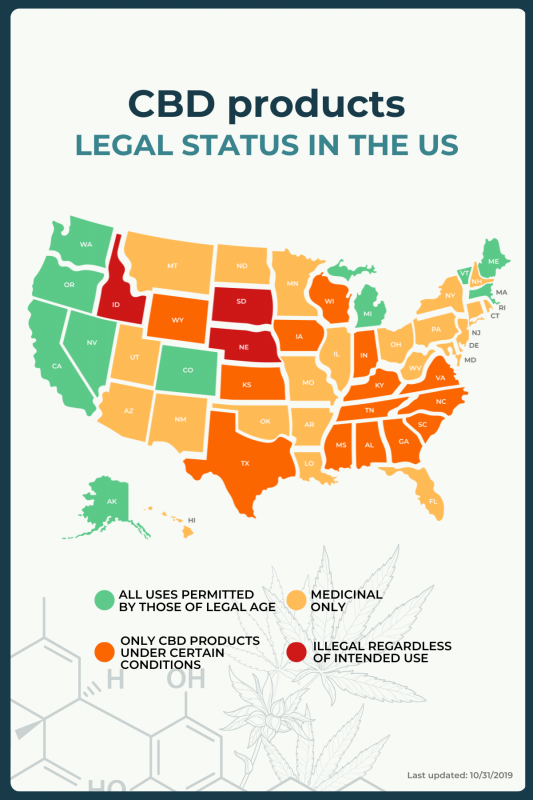
“Green” states are those that permit all uses of cannabis and cannabinoids by anyone of legal age.
“Amber” states are those that have legalized medical marijuana and cannabinoids; a prescription is required for use.
“Amber-red” states are those that permit only CBD products obtained from hemp only under certain conditions, including for medical purposes. For some states in this group, these products can only be used under the supervision of a medical professional.
“Red” states outlaw all cannabis and cannabinoid products, regardless of intended use.
CBD Oil Review has information on laws regarding cannabis use in each state.
In Europe and the U.K., although laws vary from country to country, most have now legalized the use and sale of CBD products.
In Canada, the situation is not quite so clear. Although the country legalized recreational cannabis last year, many CBD products were not included in this legislation. According to a statement from Canada’s Department of Justice, cannabis edibles and concentrates will be legal for sale approximately one year after the Cannabis Act took effect on Oct. 17, 2018.
How is CBD taken or applied?
CBD is available in different formulations, including oral capsules, oral sprays, intranasal sprays (using a mist-type dispenser like in some allergy medications), and oils.
CBD oil is one of the most common formulations. It is made up of CBD, along with a carrier oil such as coconut or hemp seed oil. It can be taken as a tincture under the tongue, ingested by adding it to food or drink, or applied topically on the skin.
Formulations can also be taken using a type of e-cigarette device. This type of application was the intense focus of news reports in the U.S. throughout 2019, due to vaping formulations largely thought to contain THC as well as lung-damaging additives like vitamin E acetate. Hundreds of people have become ill, and more than a dozen have died. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration both recommend against vaping in light of these concerns.
It is not clear whether all CBD formulations are equally effective, and there is some debate over which formulations might be most effective in potentially treating the symptoms of MS.
Can CBD reduce MS symptoms?
Some evidence suggests that CBD may be able to ease MS symptoms, at least for some patients, but the benefits of cannabis use in people with MS are still under investigation. The available data indicate that a cannabis extract with a roughly 1:1 CBD to THC ratio used as an oral spray may reduce pain and muscle spasms in MS patients.
Still, more research is needed to determine whether readily available CBD products such as oils, sprays, and edibles can provide MS symptom relief, and to better understand if any harm exists in using them.
In the U.S., the Federal Trade Commission sent letters to several companies recently, warning them against advertising that their CBD products can cure, prevent, or treat diseases, including MS. The companies were not identified.
Are all CBD products the same?
There are many formulations containing CBD available online and through other sources. However, the illicit nature of the CBD market means that not all formulations are the same or even contain what the label indicates.
A study conducted by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine in 2017 reported that of 84 CBD products purchased online, more than a quarter contained less cannabidiol than indicated, and 18 contained THC. Nearly 70% of the products in the study were mislabeled, according to the researchers.
This variability makes it very difficult to achieve a consistent dosage and to assess how effective any of these products may be.
What are the side effects?
In general, CBD is well tolerated, but it can cause side effects that include dry mouth, diarrhea, reduced appetite, and fatigue. The compound can also interact with some medications, including blood thinners.
It is very important to discuss with a doctor before using cannabis, THC, or CBD products, even if legal, to treat disease symptoms.
Are there any approved medications containing CBD?
The FDA has not yet approved any cannabidiol formulation for the treatment of MS. To date, it has approved one CBD-based medication to treat epilepsy, and two CBD-derived medications to treat symptoms related to AIDS.
In the U.K. and several other European countries, a medication called Sativex (nabiximols) has been approved to treat muscle spasms in MS; the company that developed this therapy is conducting clinical trials in the U.S. to possibly request approval from the FDA.
Last updated: Oct. 31, 2019
***
Multiple Sclerosis News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.


